Like last week, this week’s theme continues to be vulnerabilities, discovered months ago, that are still rearing their head. A July Microsoft SharePoint issue has been added to the Cybersecurity Infrastructure and Security Agency’s catalog of known exploitable vulnerabilities. Additionally, VMware released a patch for an already-patched vulnerability from last month due to an insufficient heap overflow fix.
We’ll also look at increased phishing attacks, a couple of different Cisco flaws, and a Fortinet vulnerability that took some time to get its own CVE. As always, set a patching cadence for your organization so fixes aren’t pushed to the back burner, and make sure your newer security personnel understand the importance of immediate patching.
October 21, 2024
VMware Re-Patches September Vulnerability
Type of vulnerability: Heap overflow and privilege escalation.
The problem: VMware released patches for its vCenter Server software, which manages vSphere virtual computing environments. One of the patches is for a vulnerability that I mentioned in a recap last month, a critical heap overflow issue. The flaw wasn’t completely solved in the first patching round and must be addressed further. The bug could lead to RCE if exploited through a specially crafted packet.
This vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2024-38812 and has a base score of 9.8.
The related vCenter flaw, CVE-2024-38813, allows a threat actor to escalate their privileges to root using a specially created network packet. Broadcom also mentioned the patches for this vulnerability in its security bulletin and recommended patching. Broadcom also released patches for the 8.0 U2 line of vSphere for customers who already use that version.
The fix: Download the appropriate fixed version, based on your existing version of vCenter Server, from Broadcom’s list of patched software.
October 22, 2024
Samsung Zero-Day Could Allow Privilege Escalation
Type of vulnerability: Use-after-free.
The problem: A zero-day use-after-free vulnerability in Samsung Mobile Processor’s m2m scaler driver could lead to privilege escalation. Google researchers Xingyu Jin and Clement Lecigene recently provided exploit information on the bug as part of Google’s Project Zero. According to NIST, the vulnerability also affects Wearable Processor Exynos 9820, 9825, 980, 990, 850, and W920.
The flaw is tracked as CVE-2024-44068.
The fix: Samsung patched the vulnerability earlier in October. Upgrade your Samsung device to the most recent fixed version to prevent exploitation.
SharePoint Flaw Added to CISA KEV Catalog
Type of vulnerability: Deserialization.
The problem: A Microsoft SharePoint vulnerability initially made public in July was just added to the CISA’s Known Exploitable Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog. Federal Civilian Executive Branch agencies must fix it by November 12. Proofs of concept for the exploit are also available, increasing the danger of an attack.
The attacker must be authenticated and have Site Owner permissions to conduct the attack, but with those, they could inject and execute arbitrary code in SharePoint Server contexts.
The flaw is tracked as CVE-2024-38094 and has a 7.2 base score.
The fix: Download one of Microsoft’s provided security updates.
Feeling overwhelmed by all the bugs you have to keep track of? Consider using a vulnerability scanning tool to identify issues your team might not know about.
October 23, 2024
Cisco Patches Flaw That Could Lead to DoS Attacks
Type of vulnerability: Resource exhaustion, potentially resulting in denial of service.
The problem: Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) and Cisco Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) both have a vulnerability in their Remote Access VPN service. The vulnerability is a resource exhaustion issue that could lead to a denial-of-service (DoS) attack when a threat actor sends excess VPN authentication requests to the service. Remote, unauthenticated threat actors can exploit the flaw.
The vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2024-20481 and has a base score of 5.8. In its security advisory for the issue, Cisco has provided indicators of compromise that customers can use to look for a potential attack.
The fix: All users should consult Cisco’s Security Advisories page to determine which recent software version they should upgrade their product.
More Cisco News, This Time for a Critical Flaw
Type of vulnerability: Command injection.
The problem: The same day Cisco published the advisory for CVE-2024-20481, it also notified about a critical flaw in the Cisco Secure Firewall Management Center. The software’s web-based management interface has a vulnerability that could allow a remote threat actor to execute arbitrary code as root on the operating system.
The vulnerability stems from flawed input validation for HTTP requests. If a threat actor specifically creates an HTTP request targeted at a certain device, they could then perform RCE.
Valid user credentials are required to exploit a read-only Security Analyst role. It’s also possible that a threat actor could execute remote code on Cisco Firepower Threat Defense devices.
The fix: Download the appropriate fixed version from Cisco’s Security Advisories page.
Netskope Reports Increase in Webflow Phishing Pages
Type of attack: Phishing and subsequent credential theft.
The problem: Netskope has reported a significant uptick in traffic to Webflow-based phishing web pages. Netskope Threat Labs observed this increase from April to September 2024 and found that the main targets are crypto wallets like Coinbase and credentials to webmail platforms like Microsoft 365.
“Attackers abuse Webflow in two ways: Creating standalone phishing pages and using Webflow pages to redirect victims to phishing pages hosted elsewhere,” said Jan Michael Alcantara, one of Netskope’s researchers and the post’s author.
Custom subdomains, one of Webflow’s features, can be exploited to falsify login pages, and the threat actors use Webflow’s legitimate link or form blocks to steal credentials once they’re entered. Some attackers could build a phishing page and steal credentials without writing any code.
Alcantara and his colleagues used a Webflow free account to test how easy it was to create a phishing page and were able to make one within five minutes.
“If the situation requires, Webflow also provides the means to redirect stolen credentials to a separate attacker-controlled website,” Alcantara said. “Webform will forward the filled-up form using the URL added to the submit button action field.”
The fix: Check URLs for the malicious domain *.webflow.io, which indicates a phishing site. Additionally, Netskope recommends that organizations inspect all HTTP and HTTPS traffic and use remote browser isolation technology to avoid malicious websites.
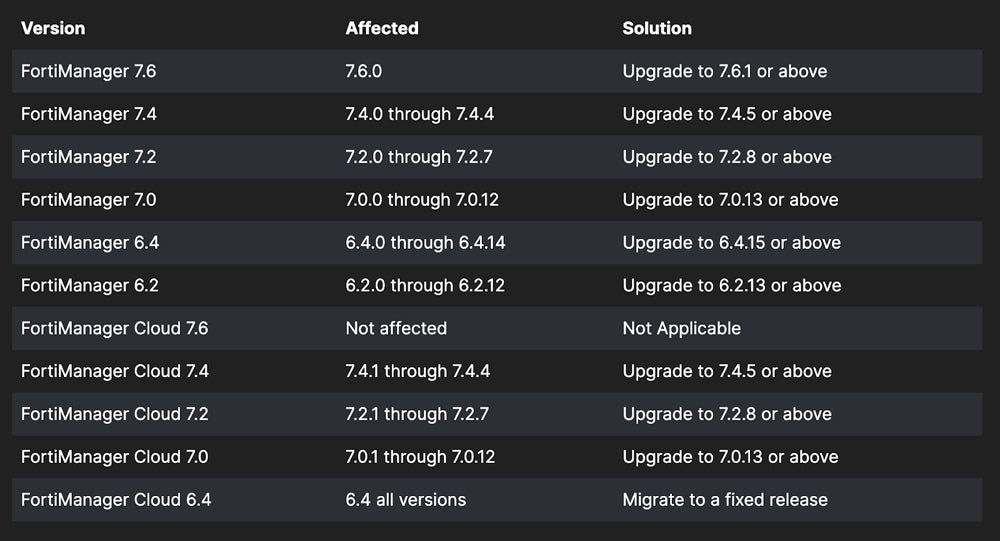
Mysterious Fortinet Vulnerability Finally Receives a CVE
Type of vulnerability: Missing authentication leading to RCE.
The problem: Security researcher Kevin Beaumont learned that a formerly undisclosed Fortinet vulnerability, with no CVE, affected the FortiGate to FortiManager protocol. He waited for some time to post his public blog about the flaw, trying to give Fortinet time to manage the threat before it was widely known. Beaumont dubbed the vulnerability FortiJump and noted it’s supposedly been used by nation-state actors.
On October 23, Fortinet released a security notice for the vulnerability and labeled it CVE-2024-47575. The issue is a missing authentication for critical function vulnerability. It could allow an unauthenticated threat actor to execute remote code using crafted requests if exploited.
The fix: Fortinet provides the following table of affected software versions and their appropriate upgrades:
Read next:




